Going international? You'll need to learn how to streamline your international payment process. This guide dives into the advantages of international payment methods for SaaS companies.
Whether you're a SaaS startup or an established enterprise, it’s vital to learn how to streamline your international payment process. It's time to help your business to grow.
This blog will examine the advantages of international payment methods for SaaS companies.
We will compare the pros and cons of the most commonly used options. From credit cards to e-wallets, we'll take a closer look at what each option has to offer. This will help you to determine which one is right for your business.
Why should your business consider enabling international payments?
Expanding your business globally can be a significant opportunity for SaaS growth. However, to succeed in international markets, you need to be able to accept payments in the local currency and preferred payment methods of your customers.
Enabling international payments can provide your business with many benefits, including:
Increased revenue
Accepting payments in local currencies and preferred payment methods makes it easier for customers to purchase your product or service. This can lead to increased sales and revenue for your business.
Access to new markets
Accepting international payments can allow you to expand into new, previously inaccessible markets. By removing barriers to purchase, you can tap into new customer bases and grow your business.
Enhanced customer experience
Providing customers with their preferred payment methods and currency can improve their experience with your business. It shows that you understand their needs and are willing to make the buying process as seamless as possible.
Competitive advantage
By offering international business payments, you can gain a competitive advantage over businesses that don't. This can make your business more attractive to customers and help you stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Examples of successful global expansion
Several of Paddle's customers have successfully expanded their business globally by implementing international payments.
For example, Kaleido used Paddle to launch and scale their remove,bg tool globally. They implemented a complex billing model and sold in over 20 native currencies without integrating any other revenue tools. They rose from zero to 4,800 paying customers from 119 countries within six months of launch. Then to 43,000 customers from 181 countries within 18 months of the software launch.
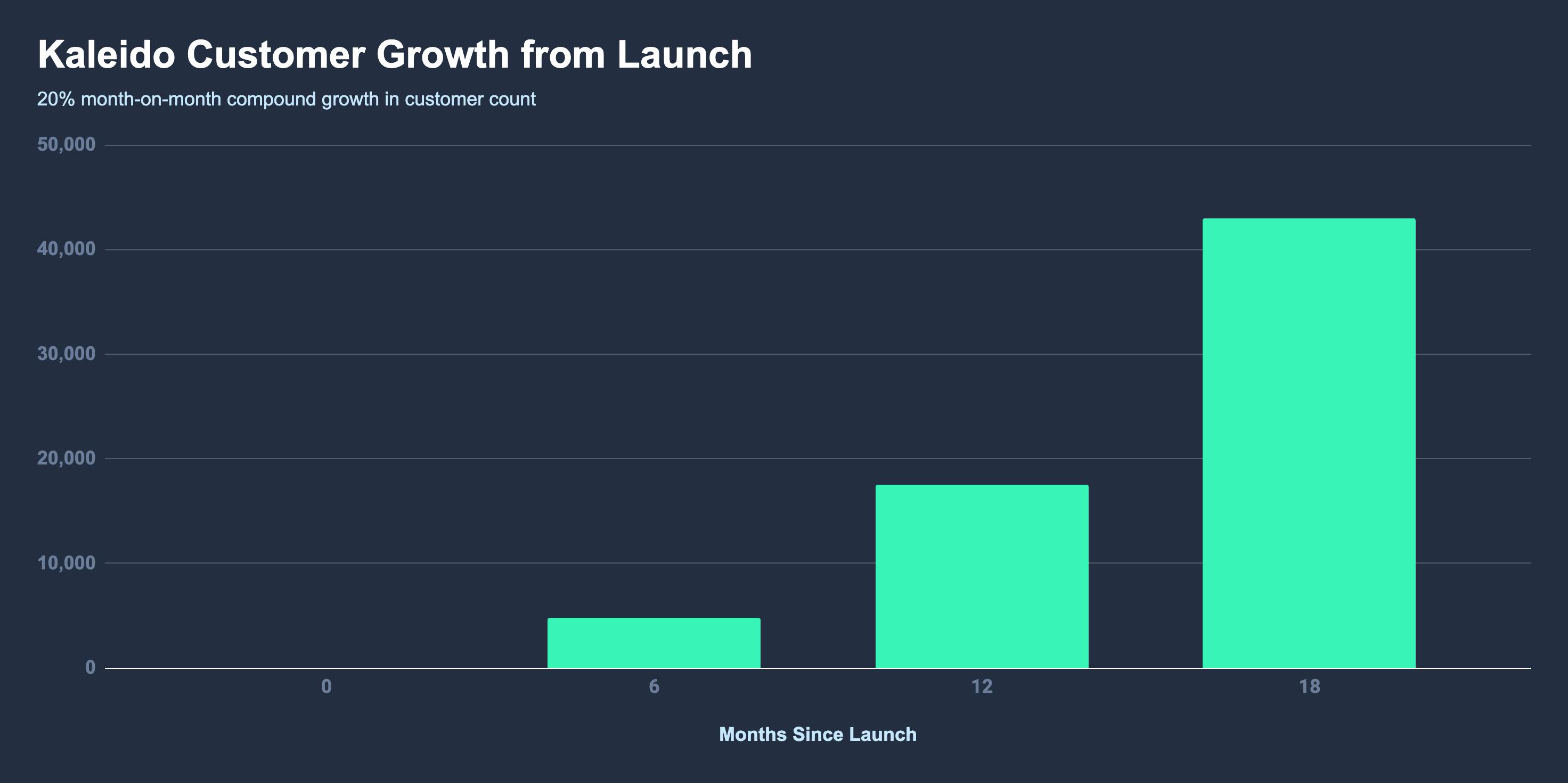
By offering local payment methods and currencies, you can expand your business globally and tap into new sources of revenue.
Why are international payments important for small businesses?
Any business that runs imports or exports or purchases inventory, materials, or goods internationally requires a means of making payments internationally. Even though COVID-19 and global instabilities still impact markets, imports and exports remain high as businesses take advantage of favorable exchange rates and global economies of scale to reduce their costs.
Globalization has given businesses access to international goods and labor and provided businesses with the ability to sell to any customer and any market anywhere in the world. This does not mean that cross-border payment systems are simple. Making or receiving payments from abroad can be complicated, with multiple currencies and charges to consider.
While many new forms of payment have cropped up promising simple and safe methods of transferring funds internationally, not all are legitimate, especially the numerous unregistered fintech companies, e-money apps, wallets, and decentralized blockchain players have appeared in the last few years.
Top international payment methods for 2023
What comes to mind when you think about international wire transfers? Expensive? Complex? You’re not wrong.
Traditional banks often charge hefty inter-bank rates for foreign currency transfers. These rates depend on the currencies and amounts being exchanged.
Unfortunately, international trade methods of payment are unavoidable, even for small businesses. A globalized workforce, competitive global supply chains, networks, and globally dispersed vendors mean that even SMBs have to transfer funds internationally at some point.
In this article, we’ll look at the most popular and secure methods of payment businesses can use when transacting internationally.
Cash-in-advance
Payment methods:
- Cash Payments
- Debit cards
- Wire transfer
- Bank transfers
- ACH
- Digital Payments
- Smart cards
Pro and cons: Cash-in-advance payments are low-risk for sellers as payment is made before goods are received. Buyers’ cash flow may be impacted negatively by this form of payment.
Credit
Payment terms: 30, 60, 90-day open account.
Payment method: Consignment
Pros and cons: This method offers enhanced cash flow for the buyer, although there is no guarantee of payment for the seller. Sellers can reduce the cost of managing and storing inventory, although the delay in payment may increase the risk of non-payment.
Bank remittance
Payment methods: Letters of credit documentary collection.
Pros and cons: The bank acts as the facilitator in the deal. In the case of LCs, the bank offers verification, lowering the default risk. However, both methods are expensive and time-consuming to manage. Currency fluctuations may impact profits.
International payment terms and payment methods
Particular attention should be paid to specific payment terms and pricing analytics when making international payments. Exporters should take care to prepare the correct documentation and perform rigorous checks on customers to determine their creditworthiness. Choosing a secure and straightforward method is essential when conducting international trade. Even the slightest mistake can lead to delays.
Cash-in-advance payment terms
Receiving cash in advance of goods being shipped is seen as a low-risk global payment method and, therefore, the most desired by exporters and e-commerce businesses, especially if the risk of non-payment is high. There is no risk of default, and the exporter can provide a refund or credit without concern about the payment being withheld.
Cash payments, debit card payments (visa or MasterCard), direct debit, wire transfers, bank transfers, escrow services, e-wallets, credit card payments, digital payments and smart cards are commonly used. Alternative payment methods include telegraphic transfers, paper checks and automated clearing house payments.
There are a few pros and cons to this method. The customer or distributor may not be able to make payment in cash in advance as paying cash for goods can impact cash flow negatively. Buyers may be concerned that they will not receive their goods, which means that businesses trading on cash-in-advance terms only may lose customers to competitors with more flexible payment terms.
Credit payment terms
Under credit payment terms, businesses can pay for goods several weeks or months after receiving them. Open account and consignment terms are the most common credit payment methods in international trade.
Open account transactions are sales where goods are shipped and delivered before the payment is due. These terms are typically 30, 60, or 90 days in international sales. This is an advantageous payment option for payers (especially in terms of their cash flow and cost) but a high-risk option for the seller. Consider this option alongside the importance of your SaaS positioning.
This doesn’t mean open accounts are not commonplace, however. Open account terms are quite common abroad, and exporters who aren’t willing to explore this option risk losing sales to competitors. Exporters will usually mitigate the risk of non-payment through export credit insurance or other trade finance techniques.
Consignments are a variation of the open account terms. Payment is sent to the exporter after goods have been sold to the end customer by the foreign distributor. International consignments are based on contractual arrangements whereby the distributor receives, manages, and sells goods on behalf of the exporter.
Exporters are not guaranteed payment, and their goods are out of reach in the hands of a foreign distributor or agent, which poses considerable risk. However, goods are readily available and ready for rapid delivery in the market, which comes with considerable brand and business benefits. It can also reduce the cost of storing and managing inventory.
The key is to always partner with a trusted distributor and ensure that the appropriate insurance is in place for goods in transit or in possession of the third party.
Bank remittance
While individuals and business entities may be hard to trust at times, banks are financial institutions, synonymous with international compliance, security, and credibility. Companies that have doubts about a foreign buyer but are satisfied with the reputation and creditworthiness of the buyer’s bank may use payment methods that include letters of credit (LCs) or documentary collection (D/C).
A bank will guarantee payment for a customer's purchase, as long as all requirements are met and documented, by issuing a letter of credit. The buyer establishes credit and makes payments to their bank account to utilize this service. A letter of credit offers the buyer protection, as there is no payment obligation until the goods have been shipped according to the terms of the agreement.
Unfortunately, this method is expensive and time-consuming, during which time currency fluctuations can negatively impact profit margins.
In documentary collection, the exporter's bank (the remitting bank) is responsible for collecting the payment for the sale, and sends the relevant documents to the importer's bank (the collecting bank) for the money to be released. The importer's funds are then sent to the exporter.
In this scenario, the bank acts as a facilitator, but they do not offer verification or recourse for non-payment. This method is less costly than letters of credit, but there are significant risks, including the risk of paying return transport costs if the buyer becomes unwilling or unable to pay.
Use Paddle to offload international payment complexities
While there are many different ways of making payments internationally, some are extremely complex, with hefty fees and confusing currency exchange requirements. Others are so time-consuming that currency rate fluctuations may impact your sale while you wait for payment. Then there is the huge frustration of international payment failure.
Launch your SaaS business internationally without having to worry about the headaches of localization, different currencies, payment providers or tax compliance.
Working with Paddle means you can choose from a range of ready-to-go localized currencies. Use Paddle’s simple and secure system to accept payment methods, from local, like Alipay, to B2B, like wire transfers.
Businesses with a globalized workforce can process more and more transactions without having to worry about sales tax implications or creating more admin for the team. Tax reporting on international spending, like VAT and GST paid on international purchases, is taken care of by Paddle.
Localize your branded inline checkout experience for your global customers without the complex functionality of integrating a host of payment gateways and losing weeks to complying with new tax regimes. Achieve faster, pain-free international growth, open up new revenue streams and get a competitive head-start with payments through Paddle.
FAQs
What is an international payment method?
An international payment method is a transfer of funds that crosses national borders and involves different currencies, e.g., US dollars (USD) and Pounds (GBP), USD and Australian Dollars (AUD).
What are the best methods of payment for international transactions?
Exporters may prefer cash-in-advance payment methods, including credit cards, wire transfers, escrow, or paper cheques; importers may choose open accounts or consignment payments. Businesses should opt for a method with low or no foreign transaction fees, capable of multi-currency transactions. Be sure it won’t over-inflate customer acquisition costs and cause issues with your SaaS metrics for valuations.
Who should offer international payment methods?
Any business that wishes to take advantage of international suppliers, expand to a foreign market or audience, or hire a global workforce needs to offer some form of international payment.
Can international payments be risky?
The risk of fraud when payments are made to verified or known suppliers is generally low. However, some payment methods come with currency exchange variations, delays, and hefty fees that can impact profits and pose a risk to the business. It’s always best to opt for an online payment method with zero foreign transaction fees and clear payment terms.




