Learn about churn analysis, including 6 essential ways to analyze churn for SaaS, the key metrics that matter, and why you can’t afford to overlook the role of payments in churn.
All SaaS businesses share a common enemy: churn.
Defined as the percentage of customers that cancel their subscriptions in any given time period, churn rate is an essential metric that can make, or break, the success of your SaaS business.
That's why it's so critical to master churn analysis. No SaaS company can hang on to all its customers forever. But, by understanding the nuances of why your customers churn, you can find more effective ways to reduce it.
After all, there’s nothing worse than diving in to fix a problem without knowing exactly what’s causing it.
In this guide
- What is churn analysis?
- The importance of calculating churn
- Why calculating churn is so hard
- Why churn analysis is important for SaaS businesses
- 6 ways to analyze churn
- The importance of cross referencing metrics
- Retention rate vs churn rate
- Gross revenue retention vs net revenue retention
- Churn analysis FAQs
What is churn analysis?
Churn analysis refers to the analysis of factors affecting the churn rate of a business. It helps evaluate customer data to better understand customers’ needs and see if your company is meeting them. The results of a customer churn analysis help decide how to allocate resources and make improvements to reduce customer attrition and boost retention.
The importance of calculating churn
First, let's zoom in on the numbers. Why is it so important to calculate churn?
Churn has a resounding impact on your business. In short, lost customers means lost revenue. What's more, the cost of getting new customers can be five times higher than the cost of keeping existing ones. Excess churn is terrible for your bottom line.
Reducing churn means playing the long game. Lots of little improvements add up to better overall performance. With churn, the laws of compounding are on your side.
Churn affects more than just your business metrics. Churn rates also show you a bit about your customer experience and whether your customers are getting value from your product or service. If your churn rate is high, it indicates that something is going wrong with this relationship.
Customers who churn because they're not getting value can damage the business in the long run, such as by negative word-of-mouth or online reviews.
In short, you really can't afford to skip churn analysis.
Why calculating churn is so hard

Businesses typically use the following formula to calculate churn:
Number of cancellations per time interval /
Number of customers at the beginning of the time interval
Churn analytics and calculation may seem simple in essence. But in practice, there are several different types of churn and several ways to define churn in the SaaS industry:
- Customer level churn, where the customer cancels their account entirely, meaning they end their relationship with your company.
- Subscription level churn, where the customer stays with you, but they downgrade their subscription service level (they might also upgrade it).
As well as these different levels of churn, other factors play a role in influencing churn rates. Churn can be seasonal; you might find that it changes during certain months.
Certain types of customers may churn more frequently than others. And finally, certain subscription levels may retain customers better than others.
As you can see, churn can be complicated.
One recommended method involves taking an average churn rate for every day of the month, then dividing it by the average customer count during that same period of time.
Here’s our explainer of how to calculate churn rate.
Why churn analysis is important for SaaS businesses
Analyzing churn is essential for any SaaS business, but many overlook it, seeing it as a sign of failure. But rather, churn should be viewed as a prime opportunity to learn and improve.
Churn analysis allows you to evaluate strengths and weaknesses in your existing processes, while improving your ability to deal with, and prevent, future churn.
Losing a few customers may seem insignificant at first. But churn is a metric that compounds over time. That’s why it's a good idea to conduct a churn analysis whenever you notice something out of the ordinary with your churn rate and if there are any at-risk customers.
Financial metrics are the first area of business that churn affects. Let's examine these metrics one by one.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
Customer cancellations directly affect your MRR. To clarify this, you can calculate a metric called churn MRR rate, which provides a percentage for the impact of churn on your business.
First add up the MRR of lost customers over a given time period, then divide this number by MRR for the same time period.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
The cost of attracting a new customer is always more than maintaining an existing one. LTV is the total value of your customer over the entire length of their relationship with your company.
It's common for new SaaS companies to focus too heavily on acquiring new customers rather than keeping the existing ones.
That’s a mistake.
If your SaaS churn rate is too high, you'll have to invest substantially in attracting new customers to match the ones you're losing. It makes more sense to tackle the churn rate first.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
This metric tells you how much you need to spend to acquire a new customer. As we already learned, it typically costs more to acquire a new one than maintain an existing one.
A high churn rate means you’ll have to spend more money on acquiring new customers, which increases your CAC.
Net Negative MRR Churn
Unlike regular churn, this churn metric is one to aspire to. Net negative churn means that total revenue from your existing customers surpasses the revenue lost to churn.
Basically, your existing customers are spending enough extra money to offset the losses from those who churned. You can reach a net negative churn rate in several ways, including by:
- Upselling to existing customers
- Customers renewing their subscriptions
- Customers upgrading their plans
Revenue Churn
This is the way to measure revenue lost as a direct result of customer churn. You can measure it either in terms of MRR or ARR (annual recurring revenue).
6 ways to analyze churn
When preparing a churn analysis, it's important to think about churn in relation to both your business and your customers. The following analysis methods will help you achieve this.
Before starting your churn analysis, it's important to ask yourself: What problem am I trying to solve? This will help guide the analysis process to avoid wasting time doing random searches in churn data and instead get some actionable insights.
To understand how to reduce churn, you'll first need to know the following:
- Which customers are churning?
- Why are they churning?
- Which customers are at risk of churning soon?
Next, make sure you have accurate subscription data to work with. Once you've got all the data in front of you, it’s time to analyze it.
1. By cohort
Cohort analysis is a good way to begin your churn analysis. In cohort reports, you segment your customer base according to a specific time period.
For example, you might decide to analyze churn according to a cohort of all customers who purchased your product in January 2021.
Cohort reports are useful because they produce numbers which are not influenced by new customer acquisition.
Smart customer segmentation also allows you to easily spot patterns in your customer base. You can easily compare different cohorts to figure out if seasonal trends affect your churn rate. The downside is that if you have a lot of cohorts, the analysis can get confusing.
2. By customer age
In this approach, you group your customers according to the length of time they’ve been with your company. Analyzing churn by age is invaluable for identifying patterns across your entire customer base without getting bogged down by too many cohorts.
For example, you could measure churn rate during the first month of subscription, second month, and so on.
If you find a higher churn rate during the first month, it might be indicative of your poor onboarding processes. Churn after 12 months could mean customers are leaving at the end of an annual contract, and the problem is at a later stage of the customer journey. You can then focus efforts on ways to encourage them to renew.
3. By geography
You can gain important context by examining your customers’ locations. For example, local tax regulations, payment processing methods, average pricing, and payment gateways vary according to country. It’s essential for SaaS businesses to comply with these rules.
If your customer base is widely spread around the world, you might be losing customers due to a lack of local payment options or lack of compliance with regulations. This is an urgent problem to address.
4. By customer behavior
Analyzing churn by behavior can reveal important patterns related to certain features of your product. Perhaps customers churn right after they use a specific feature. In that case, your product and engineering teams should dig in further to identify the issue and create a fix.
On the other hand, if certain features help to retain customers, then you should focus on further improving and promoting those. Churn analysis of behavior is also a good opportunity to gain a better understanding of customer engagement.
5. Voluntary vs. involuntary churn
There’s a critical difference between voluntary and involuntary churn. The former happens when a customer deliberately cancels or downgrades their subscription.
Customers can churn voluntarily for various reasons, including receiving bad customer service, jumping ship to a competitor, or having a negative experience during onboarding.
Or, voluntary churn could simply be down to changes in the customer’s budget situation or their overall needs. Whatever the reason, you should focus most of your strategic efforts on reducing voluntary churn.
On the other hand, involuntary churn is often due to expired or declined payment cards, lack of funds, incorrect payment information, or poor payment routing. The unfortunate customer is left none the wiser. In fact, they’d likely have stayed with you if it weren’t for involuntary churn.
The good news is, you can easily fix involuntary churn by implementing a robust payment processing infrastructure that includes smart and flexible dunning workflows.
6. Payment methods
Issues with payment methods are a major driver of involuntary churn. Yet, despite their importance, many SaaS companies continue to ignore the role of this core workflow.
Your business’ approach to taking payments and optimizing for payment acceptance is a vital aspect of driving overall revenue. Even the world’s best sales team can’t overcome a poor payment acceptance workflow.
Your payment acceptance rate is the proportion of successful payments out of the total payments attempted. Here's how to calculate it.

You can download this data from your payment processor. It's important to take a nuanced approach when analyzing it, which requires examining retried payments, failed payments, different payment methods, payments from different countries, and so on.
Here’s a detailed guide with further explanation of how to analyze and improve your payment acceptance.
The importance of cross-referencing metrics
On the surface, churn analysis seems like a straightforward undertaking. But, in reality, many factors go into the mix beyond just the simple metric of churn rate.
To truly understand the nuances of churn and calculate its impact on your business, it's vital to take a holistic approach that considers all the metrics mentioned above.
Customer retention is especially important, as it’s the flipside of customer churn. Improving retention rates not only cuts down your customer acquisition cost, but also helps you improve on the less tangible measures, such as customer satisfaction.
Taken together, improving all these metrics can help you build a comprehensive strategy to reduce churn .
The end goal? To boost your net revenue retention rate , which is fast becoming the holy grail of SaaS success measurements.
Don't forget that reducing churn is a task with compounding returns. The sooner you put a strategy in place, the sooner you’ll start seeing encouraging progress.
Avoid failed subscription payments and improve your churn rates.
The difference between customer retention rate vs. customer churn rate
First, think carefully about your customer retention rate vs. your customer churn rate. As a reminder, retention rate is the proportion of customers you've retained over a specific time period.
It's the direct opposite of churn rate. For example, if your retention rate is 80%, your churn rate will be 20%.
Here’s how to calculate customer retention rate:

Ideally, you should aim for a retention rate of as close to 100% as possible. Correspondingly, you should target 0% as the ideal customer churn rate.
But, more realistically, you should benchmark your customer retention rate according to norms for your specific area of SaaS business.
Managing your retention rate should be a primary focus for your business, because of the high cost of customer acquisition.
One way to increase your retention rate is through delivering targeted customer interactions personalized to their specific needs, such as through your email list.
Another way is by making sure your website includes a clear and comprehensive customer support section, with human customer service reps easily available.
Skip the calculations and jump straight into the churn metrics that matter most with our out-of-the-box SaaS analytics.
The difference between gross revenue retention rate vs. net revenue retention rate
These are two extremely important metrics that shine a bright light, not only on the health of your SaaS business but also on its potential for growth.
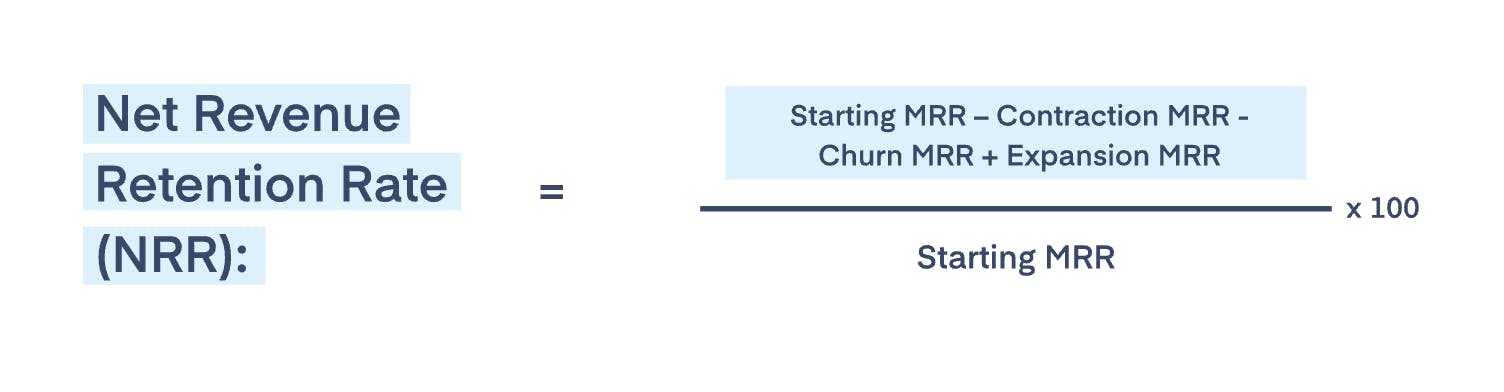
Net revenue retention rate (NRR), also known as net dollar retention, is expressed as a percentage. It incorporates several types of customer activity, including upgrades, downgrades and churn.
NRR tells you how much monthly or annual recurring revenue you’ve retained from current customers across a certain period.
That's essential because it tells you how much growth you're achieving before acquiring any new customers. It reflects customer satisfaction on a core level, which in turn is a testament to the stickiness of your product or service.
Calculate your net revenue retention rate and find out how much recurring revenue you’re losing.
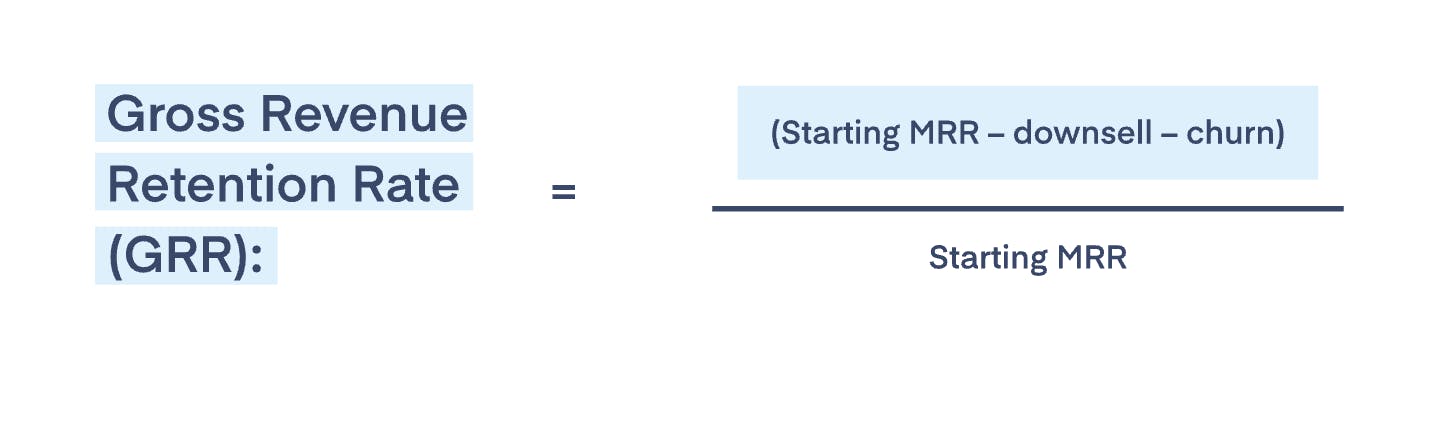
So, what’s the difference between gross revenue retention rate (GRR) and net revenue retention rate? It's simple: GRR doesn’t include upgrades or cross-sells.
That means it's always equal to or less than NRR. Ideally, to get a 360° picture of your company’s growth, you should consider both metrics.
How to calculate NRR
How to calculate GRR
Churn analysis FAQs
What is churn prediction analysis?
Churn prediction analysis is the process of discovering customers who are at risk of churn based on their previous activity. Accurate churn predictions should help businesses detect dissatisfied customers, analyze their needs more carefully, and make the necessary improvements to prevent customer churn.
What are the benefits of customer churn analysis?
Customer churn analysis helps see the total customers who stopped using your products/services over a particular period. Churn analysis can also aid in uncovering potential reasons behind cancellations.
What are churn models?
A churn model is a mathematical representation of the impact customer churn has on your business. Analyzing existing data, a churn model helps predict, to a certain degree, potential customer cancellations.


